Automated Clearing House (ACH) payments involve the electronic transfer of funds between bank accounts, facilitated by the ACH network, a secure and reliable system governed by the National Automated Clearing House Association (NACHA). It is one of the methods through which funds are transferred in United States of America.
As ACH transactions are computerized, money transfers can happen more quickly. Businesses involved in payroll processing, vendor payments, and regular transactions would especially benefit from this speed.
ACH Debits
ACH debit, or Automated Clearing House debit, refers to a type of electronic funds transfer in which funds are electronically withdrawn from a bank account to make a payment.
Parties involved in ACH Debit:
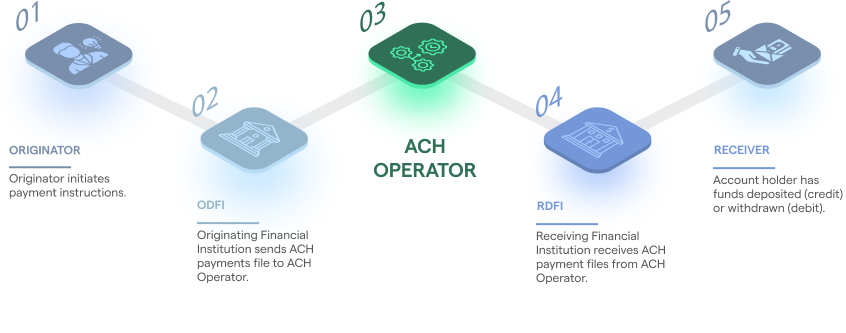
- Originator
- Originating Depository Financial Institution (ODFI)
- ACH Operator
- Federal Reserves
- Clearing House
- Receiving Depository Financial Institution (RDFI)
- Receiver
Consider the case of an electricity bill payment. Once a customer authorises a payment on a utility bill website, the utility biller will be the originator of ACH payment and the funds will be sent to Biller's bank, the ODFI. The ODFI collates and sends the file to ACH Operator. The ACH operator then sends it to RDFI because it is receiving the payment from the ACH Operator. The RDFI sends the funds to receiver.
ACH Credit
ACH credit refers to the electronic transfer of funds into a recipient's bank account. Commonly used for payroll, vendor payments, and direct deposits, ACH credits streamline financial transactions by eliminating paper checks.
Parties involved in ACH Debit:
- Originator
- Originating Depository Financial Institution (ODFI)
- ACH Operator
- Federal Reserves
- Clearing House
- Receiving Depository Financial Institution (RDFI)
- Receiver
How does an ACH payment happen?
Statistics of ACH Payments
ACH payments by volume in 2022: USD 76.7 Trillion
- Credits: USD 50.22 Trillion
- Debits: USD 26.5 Trillion
Key Metrics:
- Business to Business payments: USD 52.53 Trillion
- Person to Person payments: USD 448.53 Billion
- Consumer Bill payments and other debits: USD 9.49 Trillion
- Direct Deposits: USD 13.67 Trillion
Timelines of ACH
Same-day ACH guarantees the settlement on the same day, however, it may come with a higher price. Payments made using standard ACH are settled in one to three business days.
Advantages of ACH
- Cost-effectiveness
- Enhanced Security
- Convenience and accessibility
The ACH Network, has consistently enhanced its capabilities and transaction types, boosting processing speeds, and extending operating hours. It operates 23¼ hours each business day, settling payments four times daily when the Federal Reserve's settlement service is open. ACH is a popular system for batch processing electronic payments, providing cost-effective and flexible solutions for businesses and individuals.
However, ACH Networks have a delayed processing time because of the batch processing as compared to real-time settlement networks like Fedwire which is preferred for transactions which requires real-time settlements but comes with a cost more than ACH.
ACH payments are primarily carried out from one US bank account to another US bank account. PayGlocal supports ACH payment collection for Indian merchants by provisioning a multi-currency account in the name of the merchant to collect payments locally from their customers.



